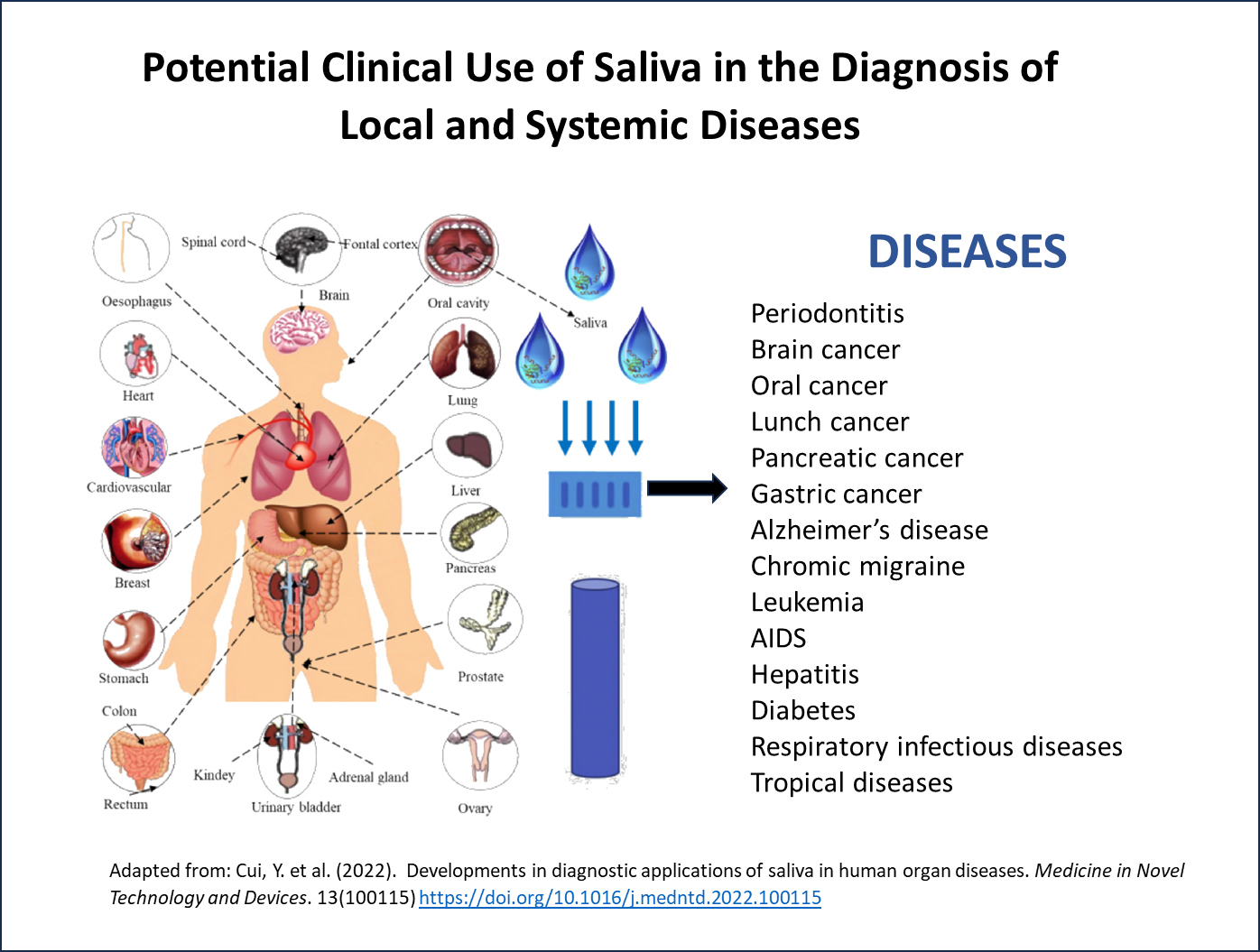
Point-of-care (POC) 诊断处于现代医疗保健的前沿,为早期疾病检测和监测提供了快速便捷的解决方案。唾液检测是 POC 最近取得的一项重大进展,它有可能使 POC 检测更加方便、高效。唾液常被称为 "身体的镜子",其中含有一系列生物标志物,包括 DNA、RNA、蛋白质和代谢物,因此是呼吸道感染、性传播疾病、热带疾病、激素紊乱和癌症等一系列疾病的理想样本。
Point-of-Care (POC) 诊断革命
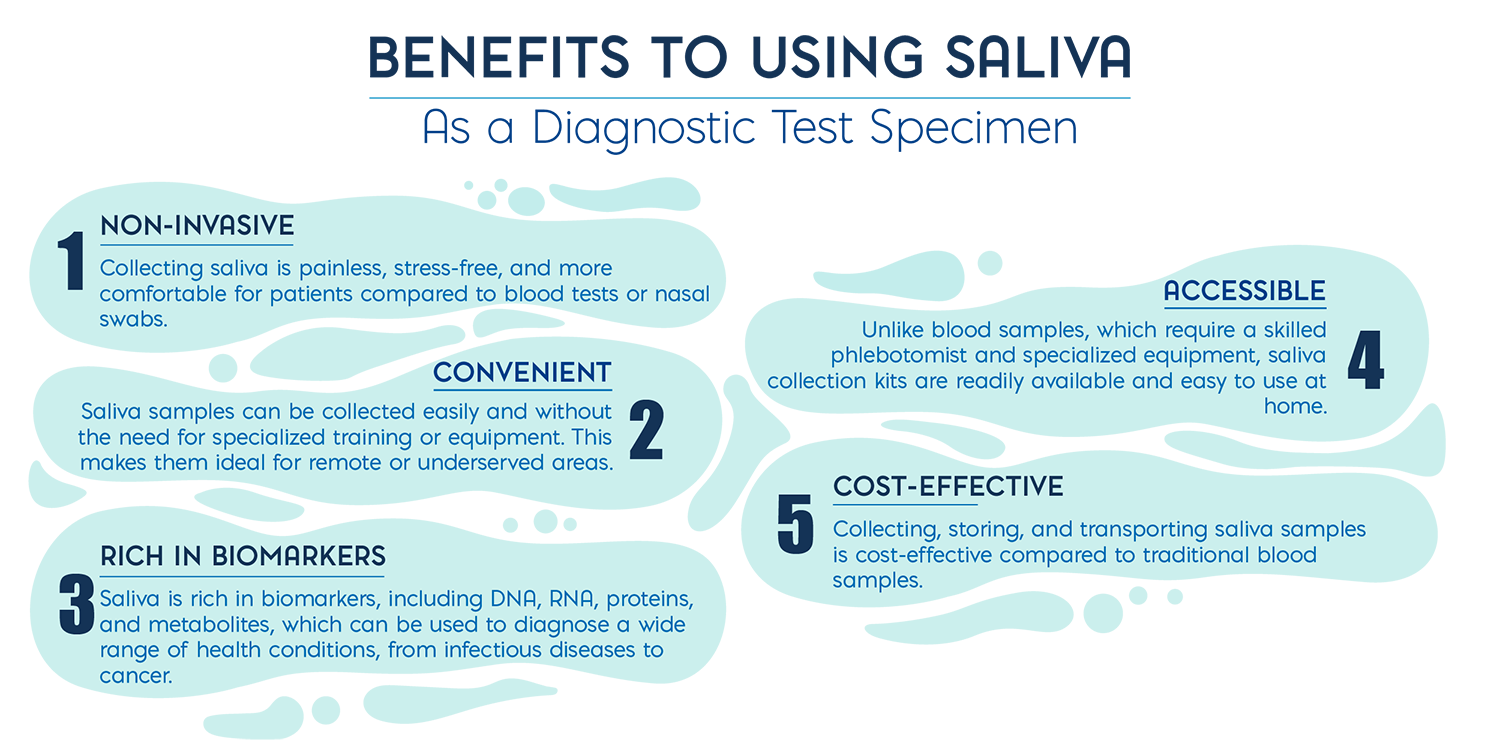
POC诊断是一种可以在传统实验室之外进行的检测,通常在患者所在地或附近进行。这些检测设计快速、方便使用,并能在 10 到 20 分钟内得出结果。样本采集对 POC 检测的准确性和可靠性起着重要作用,许多样本类型,如血液、鼻腔或咽喉拭子,都需要训练有素的专业人员来采集,并可能给患者带来不适和痛苦。相比之下,唾液取样简单,可自行取样,检测更方便,检测成本更低。因此,唾液在各种疾病的远程 POC 和家庭检测领域越来越受到关注。
唾液在POC诊断中的重要作用
直到几年前,商业唾液检测法还只能用于激素检测、艾滋病检测和药物/酒精检测。开发唾液诊断技术所面临的技术障碍之一是检测灵敏度,因为与血液相比,唾液中的分析物浓度较低(低 100 到 1000 倍)1 ,而PCR抑制物的浓度较高。但是在过去的十年中,唾液特异性分子预混液和创新的唾液采集设备等技术的进步提高了唾液样本在诊断检测中的可用性,这些设备可以有效地采集一定量的唾液,降低样本不足或样本质量差的风险。
During the pandemic, there was a significant need for widespread population testing in order to control the spread of SARS-CoV-2. Consequently, saliva was highly sought after as an alternative specimen to nasopharyngeal swabs, and several studies proved its effectiveness when used in traditional SARS-CoV-2 PCR tests and in at-home rapid antigen tests2。此外,研究发现,在重复检测中,唾液样本比鼻咽拭子更容易被患者接受3.
自新冠疫情以来,使用唾液作为检测样本已成为主流,体外诊断公司正在展示唾液在高通量仪器4 和一系列疾病检测中的用途,包括热带传染病5 、心脏病、人乳头瘤病毒(HPV)相关癌症、乳腺癌、肺癌,以及监测治疗效果、检测疾病复发和患者风险分层。目前甚至正在研究用唾液检测来检测新的生物标记物,如阿尔茨海默氏症的 tau 蛋白4.
POC诊断中的唾液特异性预混液: 改变游戏规则
POC 诊断技术正处于向更快、更方便的检测转变的前沿,与血液等传统基质相比,唾液作为检测样本更方便使用、更具成本效益,而且从采集到出结果的速度更快。然而,使用唾液作为样本类型所面临的挑战包括确保样本质量、防止污染以及实现高效的提取方法(尽管 DNA 和 RNA 浓度较低)。特别是对于分子检测来说,由于唾液中本身存在酶抑制物,因此唾液检测一直是一项挑战, 目前已有多项技术致力于改进 DNA 和 RNA 提取技术,以最大限度地减少抑制物的携带。其他技术则专注于开发耐抑制物混合物,以便能直接从唾液中进行检测,从而帮助最大限度地减少样本损失、延长检测周转时间并最大限度地降低污染的可能性。
Meridian’s Specimen-Specific™ Direct Saliva Master Mixes are one the most advanced chemistries available designed for direct detection assays from saliva samples. These mixes are optimized for sensitive and robust performance using crude saliva and are ready to use, only requiring the addition of assay-specific primers and probes. In addition, they are formulated with excipients for downstream lyophilization or air-drying to create ambient temperature stable assays which are ideal for POC applications. In comparison studies, Meridian’s Saliva-Specific Master Mixes demonstrated their significant performance advantages in efficiently amplifying RNA and DNA from extracted samples and crude saliva samples, even after the mixes had been dried down and briefly stored at room temperature.
As saliva specimens for diagnostic testing expand into new disease areas, saliva-specific master mixes for molecular assays will be a game-changer, enabling assay developers quicker development times, simpler, extraction-free workflows, and greater assay performance in terms of sensitivity and inhibitor tolerance.
To learn more about Meridian’s Specimen-Specific™ Direct Saliva mixes for PCR and LAMP applications
参考文献:
- Cui, Y. et al. (2022). Developments in diagnostic applications of saliva in human organ diseases. Medicine in Novel Technology and Devices. 13(100115) https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medntd.2022.100115
- Duncan, D.B. et al. (2023). Performance of saliva compared with nasopharyngeal swab for diagnosis of COVID-19 by NAAT in cross-sectional studies: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Biochem. 117:84-93. https://doi:10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2022.08.004
- Covid-19: Concerns persist about purpose, ethics, and effect of rapid testing in Liverpool (2020) BMJ. 371:m4690 https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.m4690
- Michaud, S. (2022). Saliva in the Spotlight. Clinical Laboratory News. Retrieved Oct 19, 2023 from: https://www.aacc.org/cln/articles/2022/janfeb/saliva-in-the-spotlight
- Diaz, J., et al. (2023). A mixed methods study assessing the adoption potential of a saliva-based malaria rapid test in the Democratic Republic of Congo. Malar J.;22(1):180. https://doi: 10.1186/s12936-023-04599-y-