55C MMLV-RT
55C MMLV-RT is a thermostable reverse transcriptase that has reduced RNase H activity and high inhibitor tolerance, delivering faster and more sensitive cDNA synthesis than any other thermostable RT enzymes.
Enhance your assay with Meridian’s ultrapure dNTPs, synthesized at a large scale from premium quality raw materials with hundreds of liters available now.
- Manufactured in hundreds of liters per year
- >99% purity (HPLC)
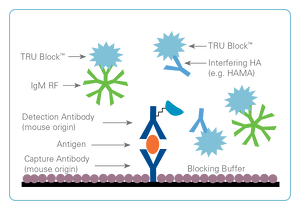
True Positive Result
In a true positive result, assay antibodies are able to freely bind to antigen present in the patient sample. Blockers help by binding to interfering substances and removing their potential to cause a false result.
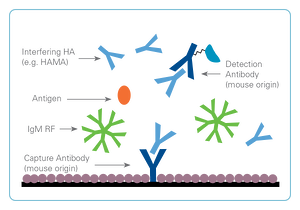
False-Negative Result
In a false-negative reaction, heterophilic antibodies bind to the antibodies in the assay, preventing them from binding to the target antigen in the patient sample. The patient sample is positive but the result is reported as negative.
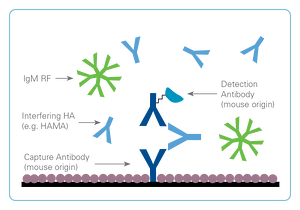
False-Positive Result
In a false-positive reaction, heterophilic antibodies bind to the assay antibodies in a manner similar to the target antigen. This causes a positive readout despite the patient sample being negative.
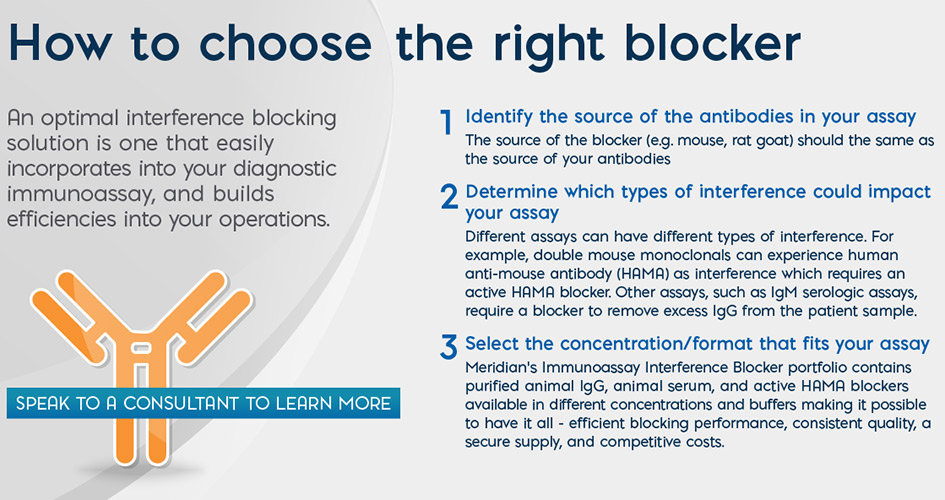
What are the Different Types of Blockers?
TRU Block™
Unique heterophilic antibody blocker that can remove many different types of heterophilic interference including HAMA and Rheumatoid factor (RF) using a completely new approach.
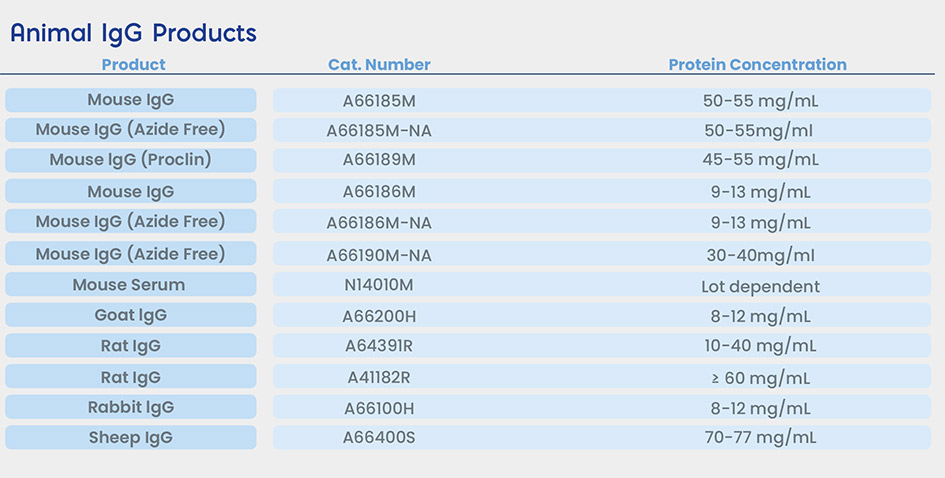
Animal IgG
Animal IgG (e.g. mouse IgG) is suitable for blocking heterophilic antibodies, especially in mixed species assays (e.g. MAb/PAb). The source of the blocker must be the same as the host antibody source.
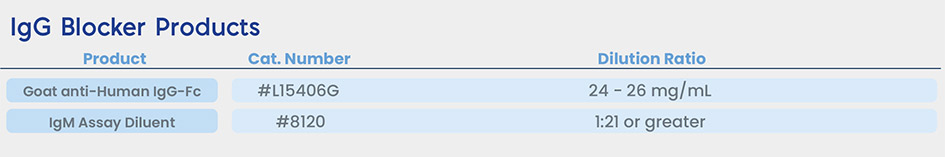
IgG Blocker
Excess IgG antibody in patient samples can interfere with IgM detection. Goat anti-human IgG and Meridian’s IgM assay diluent are designed to improve IgM assay sensitivity.
Meridian’s Portfolio of Blocker Solutions

Certificate of Analysis (COAs)
Product Highlights
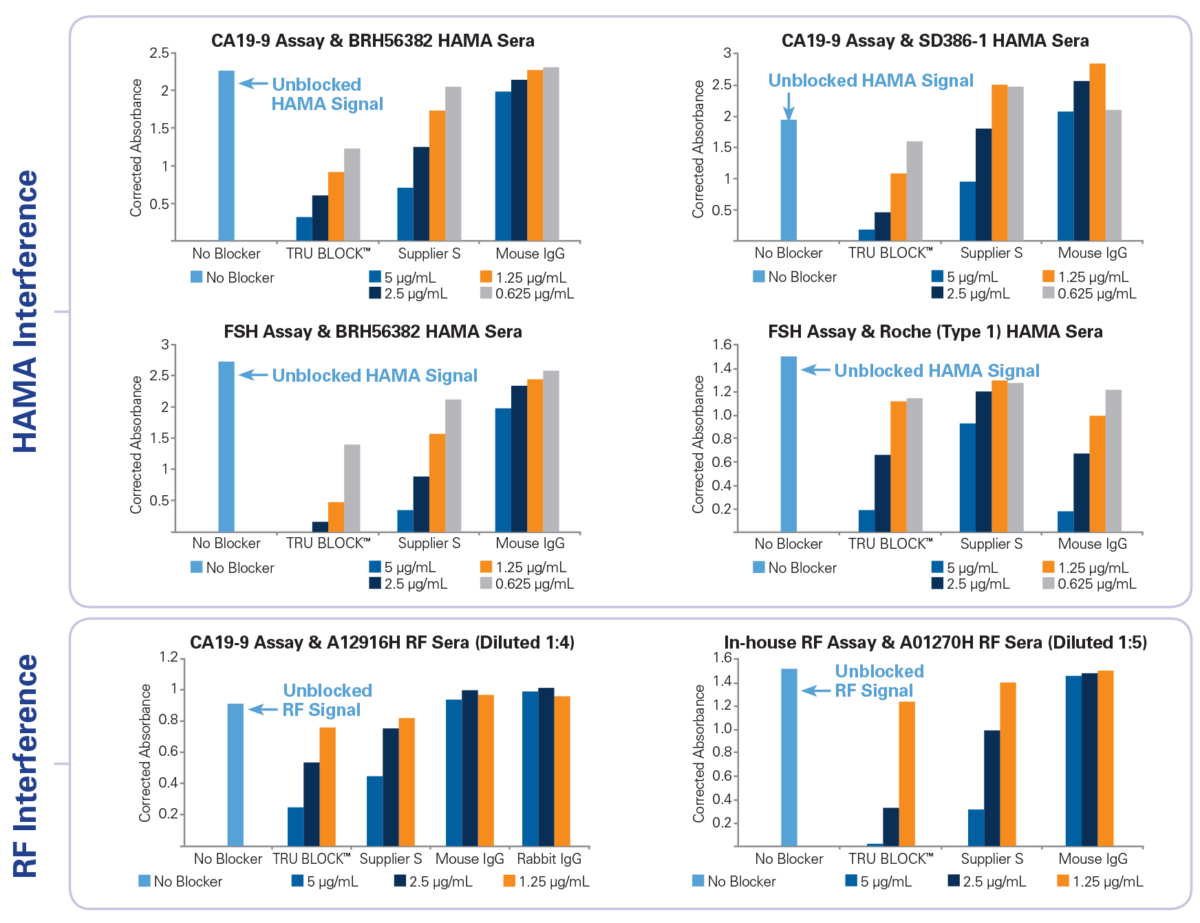
Three different double mouse monoclonal sandwich assays (a commercial CA19-9, a commercial FSH and an in-house RF assay) were used to compare the performance of TRU Block™ against mouse IgG and supplier S active HAMA blocker. To quantify the relative amount HAMA or RF activity in each human sera sample within an assay, the assay was performed as per the manufacturer’s instructions using a sample diluent buffer containing no mouse IgG or other blocker. Blocking solutions containing either TRU Block™, mouse IgG or supplier S blocker were prepared using the same sample diluent buffer at four different concentrations (5 μg/mL, 2.5 μg/mL, 1.25 μg/mL and 0.625 μg/mL). The effectiveness of each blocker was determined by the relative suppression of HAMA or RF signal (i.e. comparing the absorbance of samples with no blocker to those with various blockers). Native HAMA positive sera samples were obtained from Scantibodies, Inc. (SD386-1) and BioReclamation (BRH56382). Another sample was obtained from Roche (Roche Type 1) which contains pooled normal human serum spiked with Roche proprietary HAMA. RF sera samples (MLS Cat No. A12916H and A01270H) were obtained internally and are available for purchase from Meridian’s product catalog (www.meridianbioscience.com/lifescience). The study results demonstrate that TRU Block™ is equivalent to or better than a supplier S active blocker on all HAMA and RF sera samples tested.
Resources to Learn More

Learn More
Lead about the factors that need to be considered in selecting the right blocker for an immunoassay.

Watch a Short Video
Find out how TRU Block™ works to prevent heterophilic antibody interference.
Read Whitepaper
Gain a deeper understanding of the challenges faced by IVD manufacturers by reading the whitepaper “Reducing Errors in Immunoassay Testing”.
FAQs: Immunoassay Interference Blockers
Immunoassays used for human in vitro diagnostics (IVD) typically use animal-derived antibodies to recognize specific disease markers. Some patients have antibodies in their blood that can react with animal antibodies in the immunoassay and cause a false result. Although the frequency of these interferences is low, false-positive results have a significant negative impact on the quality and competitiveness of a diagnostic assay as well as on the lives of those individuals who have been falsely diagnosed.
Human anti-mouse antibodies (HAMA) is the most well-known antibody interference due to the wide use of mouse monoclonal antibodies in diagnostic applications. Mouse IgG can block HAMA found in patient serum.
No. HAMA only represents one type of heterophilic antibody (HA) interference – others include HA to animals such as goat (HAGA), sheep (HASA), and rabbit (HARA) which can cause false results when antibodies originating from these animals are used in immunoassays. In addition to HA there is another class of interference called Rheumatoid factor (RF), which is an autoantibody that reacts with the patient’s own immunoglobulin (Ig) and can cross react with animal Ig, similar to HA/HAMA interference.