Standard qPCR (black) and fast qPCR (blue) of a ten-fold serial dilution of template DNA
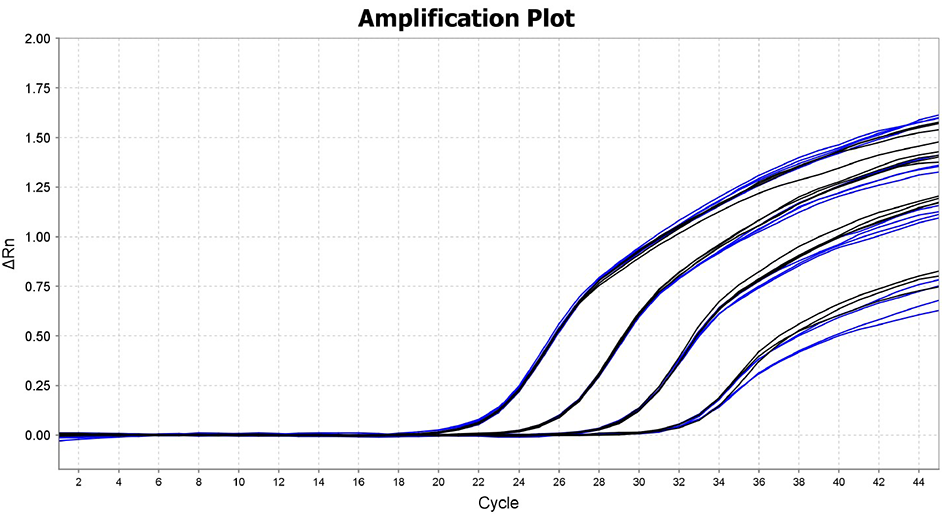
DNA target was amplified using standard qPCR cycling conditions (2 min @ 95ºC, 40 cycles of 10 sec @ 95ºC and 25 sec @ 60ºC) and the fast cycling conditions (2 min @ 95ºC, 40 cycles of 1 sec @ 95ºC and 10 sec @ 60ºC). The results illustrate the higher performance and end-fluorescence of the Fast qPCR Mix in both standard (blue) and fast (black) qPCR cycling conditions.
Fast qPCR Mix, MDX020
缓冲液化学成分、PCR 增强剂和稳定剂以及热启动聚合酶、dNTPs 和 MgCl2 的最新进展,可在快速热循环条件下获得高重复性、准确的检测结果。
文档与资源
Fast qPCR Mix, 5x, MDX072
缓冲液化学成分、PCR 增强剂和稳定剂以及热启动聚合酶、dNTPs 和 MgCl2 的最新进展,可在快速热循环条件下获得高重复性、准确的检测结果。
文档与资源
Description
Fast qPCR Mix has been designed with a highly optimized buffer chemistry and hot-start DNA polymerase, to give highly sensitive qPCR efficiency, even from low abundance targets and scarce samples. With high processivity and robustness, it delivers excellent results in both singleplex and multiplex qPCR assays and confers superior assay performance under fast thermal cycling conditions, allowing more samples to be run in a day with the highest confidence, ideal for high‑throughput assays. Fast qPCR Mix is available as a standard 2x and 5x formulation, offering flexible reaction setups and protocols.
Specifications
| Description | The latest advances in buffer chemistry and PCR enhancers and stabilizers, together with a hot-start polymerase, dNTPs and MgCl2, for highly reproducible, accurate assay results under fast thermal cycling conditions, ideal for automated, high-throughput systems. |
| Concentration | 2x and 5x |
| Appearance | Clear, colorless solution |
| Hot Start | Antibody mediated |
| Application | Probe-based, qPCR, two-step RT-qPCR |
| Sample type | cDNA, DNA |
| Presentation | 1 vial |
| Storage | -20 °C |
| Mix stability | See outer label |
| Consistency | ±0.5 Ct variance between test and reference sample |
| DNA Contamination | None detected in PCR amplification with traces overlay with the negative control on E. coli and mouse genomic DNA specific targets. |
| DNase Contamination | No detectable degradation |
产品资料
分子诊断的原料试剂解决方案分子诊断的原料试剂解决方案
FAQs: Fast qPCR Mix
Slope of standard 10-fold dilution curve indicates qPCR efficiency. The efficiency of the qPCR should be between 90–110% (−3.58 ≥ slope ≥ −3.1). If the efficiency is greater than 100%, this indicated inaccurate sample and reagent pipetting, if it is less than 100%, this indicates your samples may contain PCR inhibitors or your qPCR primer and/or probe design may not be optimal.
• Two buffers optimized for independent RT and real-time PCR
• Highly sensitive
• Recommended when the reaction is performed with a limiting amount of starting material
• More efficient because random primers and oligo d(T) can be used
• Possibility to stock cDNA to quantify several targets
When performing a reverse transcription reaction for a two-step quantitative PCR assay, it is possible to use different primer strategies. Random hexamer primers, which bind anywhere on the RNA allow full coverage of total RNA (including ribosomal, bacterial and viral RNA), oligo d(T)n (or anchored oligo d(T)n), which binds to the poly-A tail of the mRNA which is located at the extremity of the transcript, leading to full transcripts, a mixture of random hexamer and oligo d(T)n that reduces the risk of bias in cDNA synthesis and specific primers, which bind to the transcript of interest.
The ability to optimize both cDNA and quantitative PCR reactions separately and the higher cDNA yields, two-step reactions can be more sensitive than one-step reactions. The ability to separately optimize these reactions is also beneficial when performing multiplex qPCR on challenging sequences.
With two-step quantitative PCR, the use of several tubes means that it is more time consuming and less adaptable to liquid handling robotics and so more difficult to adopt for high throughput
screening assays. The use of several tubes and pipetting steps also exposes the reaction to a greater risk of DNA contamination.
Many fluorescent qPCR primer- and probe-based chemistries have been devised and are available from different commercial vendors, including:
• Hydrolysis (TaqMan) probes
• Molecular beacons
• Dual hybridization probes
• Eclipse probes
• Amplifluor assays
• Scorpions PCR primers
• LUX PCR primers
• QZyme PCR primers
The two most commonly used are:
• Hydrolysis (TaqMan) probes. The main advantages of using hydrolysis probes are high specificity, a high signal-to-noise ratio, and the ability to perform multiplex qPCR reactions. The disadvantages are that the initial cost of the probe.
• Molecular beacons. Molecular beacons are highly specific, can be used for multiplexing, and if the target sequence does not match the beacon sequence exactly, hybridization and fluorescence will not occur. Unlike hydrolysis probes, molecular beacons are displaced but not destroyed during amplification and can be used for melt curve analysis if necessary. The main disadvantage is that they are difficult to design, requiring a stable hairpin stem that is strong enough that the molecule will not spontaneously fold into non-hairpin conformations but not be too strong, or it may not properly hybridize to the target.
No, intercalating dyes bind into all DNA, this means that they cannot be used for multiplex qPCR, as different amplicons cannot be distinguished, whereas different dyes can be used on probes for different amplicons. This also makes probe-based systems more specific; only detect the gene of interest, even making it possible to distinguish between similar sequences with small differences like SNPs or mutations. In general, probe assays need less optimization, and they can be used for multiplex qPCR.
与我们的专业团队联系
想了解更多迈迪安免疫和分子产品信息?欢迎与我们联系