Sensitivity with fast cycling conditions
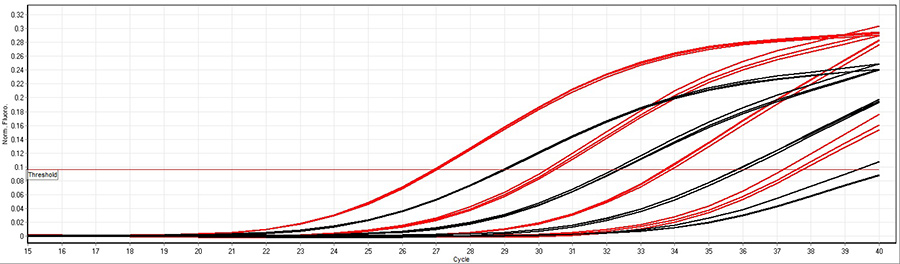
A 100-fold dilution of human cDNA was used in a multiplex assay with Low DNA qPCR Mix (red) and another supplier of chemical hot-start qPCR mixes (black) with fast cycling conditions (10 minutes 95°C followed by 40 cycles 95°C 10 seconds, 60°C 10 seconds). The results illustrate Low DNA qPCR Mix is more sensitive than other suppliers of chemical hot-start qPCR mixes in fast cycling conditions.
Low DNA qPCR Mix, MDX030
高度纯化的 qPCR 母液具有严格的化学热启动特性和低生物负载,是低拷贝细菌靶标 PCR 的理想选择,可避免假阳性扩增。
文档与资源
Description
Low DNA qPCR master mix contains a chemical hot-start Taq polymerase and highly optimized reaction buffer with dNTPs, MgCl2, stabilizers, and PCR enhancers. The Taq polymerase is purified twice, before and after the addition of the chemical hot-start, this helps to remove trace amounts of DNA (known as bioburden) that come from the manufacturing of the DNA polymerase. In addition there is no bioburden that comes with antibody hot-start, making it ideal for low-copy number targets and also microbial DNA and fungal DNA detection assays.
Low DNA qPCR master mix can also be used for fast, precise and highly reproducible genotyping of sequence variants, including loci, provides higher stringency and more specific binding of the allele-specific probes, with wider and clearer separation of allele cluster.
Specifications
| Description | A combination of the latest advances in buffer chemistry and PCR enhancers polymerase, dNTPs and MgCl2. The low DNA background and stringent hot-start properties are ideal for qPCR of low-copy bacterial targets, avoiding false-positive amplification of bacterial or fungal targets. |
| Concentration | 2x |
| Appearance | Clear, colorless solution |
| Application | Probe-based, real-time PCR, two-step RT-qPCR |
| Sample type | cDNA, DNA |
| Presentation | 1 vial |
| Storage | -20 °C |
| Mix stability | See outer label |
| Consistency | ±0.5 Ct variance between test and reference sample |
| DNA Contamination | None detected in PCR amplification with traces overlay with the negative control on E. coli and mouse genomic DNA specific targets. |
| DNase Contamination | No detectable degradation |
产品资料
分子诊断的原料试剂解决方案分子诊断的原料试剂解决方案
细菌和真菌DNA扩增细菌和真菌DNA扩增
FAQs: Low DNA qPCR mix
With a chemical hot-start DNA polymerase, the polymerase is covalently linked with chemical groups to block enzyme activity at room temperature.
Advantages
• More stringent than antibody hot-start methods, so there is no activity even for long periods at room temperature, minimizes non-specific amplification
• Low bioburden, as it is free of animal and bacterial-origin components
Considerations
• Longer activation time required for the polymerase to become fully active
Many fluorescent qPCR primer- and probe-based chemistries have been devised and are available from different commercial vendors for molecular diagnostic tests, the two most commonly used are:
• Hydrolysis (TaqMan) probes. The main advantages of using hydrolysis probes are high specificity, a high signal-to-noise ratio, and the ability to perform multiplex qPCR reactions. The disadvantages are that the initial cost of the probe.
• Molecular beacons. Molecular beacons are highly specific, can be used for multiplexing, and if the target sequence does not match the beacon sequence exactly, hybridization and fluorescence will not occur. Unlike hydrolysis probes, molecular beacons are displaced but not destroyed during amplification and can be used for melt curve analysis if necessary. The main disadvantage is that they are difficult to design, requiring a stable hairpin stem that is strong enough that the molecule will not spontaneously fold into non-hairpin conformations but not be too strong, or it may not properly hybridize to the target.
The Low DNA qPCR Mix has some inhibitor tolerance, but for amplification from crude lysates or inhibitor-rich samples we have the universal Inhibitor-Tolerant qPCR mix and for even greater sensitivity, we have the sample specific (blood, saliva, urine, stool, and plant) mixes.
Genotyping refers to the process of determining genetic variations among individuals in a population. Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) are the most common type of genetic variation and are single-base differences at a specific locus. These genotype changes can confer positive or negative phenotypic outcomes, such as more robust stress tolerance in plants or enhance the susceptibility for disease in humans. Hence, SNPs are often useful markers for understanding the biology of organisms. Genotyping is done with two allele-specific probes that have a single base mismatch and a pair of primers at each end of the SNP of interest. Depending on which base is present at the SNP position, the probe will either not hybridize correctly during the qPCR and be left intact or hybridize correctly and be cleaved to give a signal. Since the dual-labeled probe assay is based on PCR, it is relatively simple to implement, and the scale can be drastically increased by performing many simultaneous reactions together.
Genotyping also refers copy number variation (CNV), which results from having different numbers of copies of a DNA segment in various genomes. Where the copy number variation is for an encoded gene, this can lead to susceptibility or resistance to disease. This uses two sets of primers and probes, one for a calibrator gene that does not change and the other for the gene thought to have the changed copy number. A comparison to the Ct values of each allows you to determine if the copy number has changed and by how much.
与我们的专业团队联系
想了解更多迈迪安免疫和分子产品信息?欢迎与我们联系