Glycerol-Free T4 DNA Ligase (HC)
Glycerol-Free T4 DNA Ligase (HC) is a glycerol-free, high concentration enzyme (50U/µL) that catalyzes the formation of a phosphodiester bond between adjacent 5ʹ phosphate and 3' hydroxyl groups in duplex DNA or RNA. The enzyme efficiently joins blunt and cohesive ends and repairs single stranded nicks in duplex DNA, RNA or DNA/RNA hybrids.
Have questions about a product?
Contact us to learn more about Meridian’s molecular or immunoassay reagent portfolio. We want to hear from you!
Gycerol-free T4 DNA Ligase (HC), MDX200
Glycerol-free, high concentration enzyme that efficiently joins blunt and cohesive ends and repairs single stranded nicks in duplex DNA, RNA or DNA/RNA hybrids. Ideal for lyophilization.
Documents & Resources
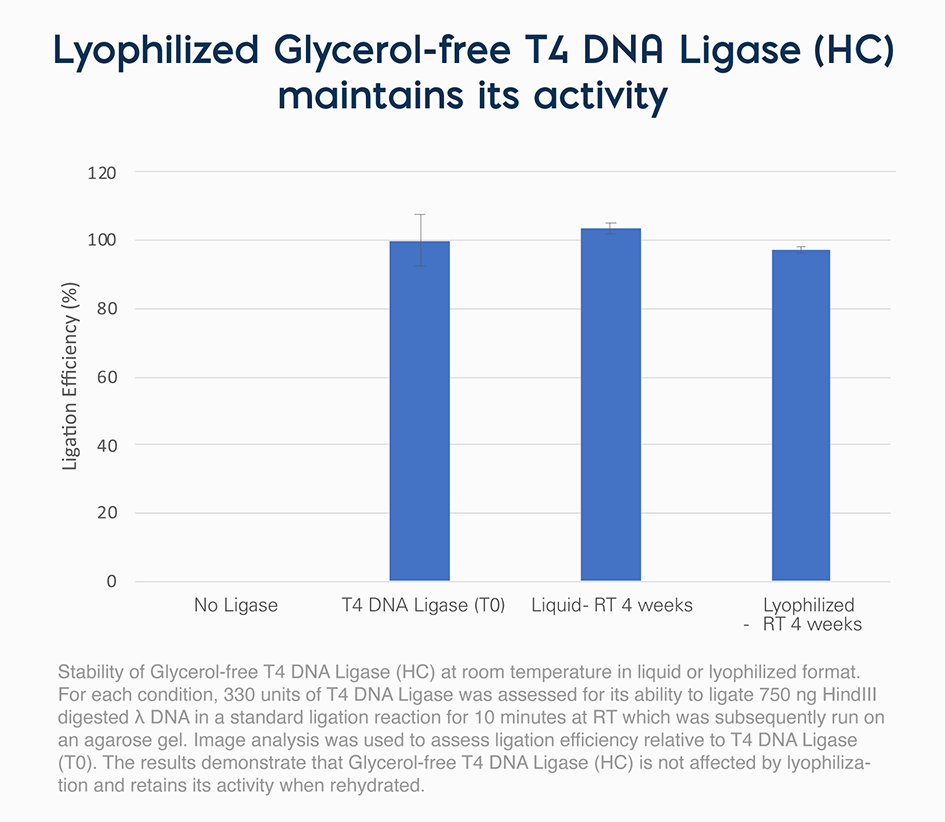
Glycerol-free T4 DNA Ligase (HC) requires a ligase reaction buffer. The concentration of Glycerol-free T4 DNA Ligase (HC) (in Weiss units) is higher than the concentration of other ligases on the market and can be lyophilized, making it ideal for microfluidics and point of care testing.
Catalogs & Brochures
Glycerol-Free T4 DNA Ligase (HC)Glycerol-Free T4 DNA Ligase (HC)
High-Specificity Pfu HS MixHigh-Specificity Pfu HS Mix
FAQs: Glycerol-free T4 DNA Ligase (HC)
T4 DNA Ligase should be used to ligate cohesive ends (10 minutes at room temperature) or blunt ends (2 hours at room temperature) or if the ligation is to be done overnight. T4 DNA Ligase should be used if heat inactivation is required. Concentrated T4 DNA Ligase is suggested for ligating single base overhangs.
One Weiss unit is defined as the amount of enzyme required to convert 1 nmol of 32P-labeled inorganic pyrophosphate into Norit adsorbable material (activated carbon) in 20 minutes at 37°C, using specified reaction conditions (Weiss, B., et al., J. Biol. Chem., 243, 4543 (1968)).
However, as the Weiss unit is not a direct measurement of DNA ligation, but an indirect measurement of the enzyme adenylation reaction, followed by determining ATP-PPi exchange, Cohesive End Unit is also used, as this is the direct measurement of DNA ligation (a Cohesive End Unit deing defined as the amount of enzyme required to give 50% ligation of Hind III fragments of lambda DNA in 20 µL of 1X T4 DNA Ligase Buffer in 30 minutes at 16°C). One Cohesive End Unit equals 0.015 Weiss units, or one Weiss unit equals 67 Cohesive End Units.
Yes, heat at 65 °C for 10 minutes.
The general formulation of a 1x ligase reaction buffer is 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.8), 10 mM MgCl2, 10 mM DTT and 10 mM ATP.
Both Mg and ATP are an essential cofactor for the reaction, two ATP molecules are consumed for each phosphodiester bond formed.
The increased concentration of the T4 DNA ligase is helpful in lower volume reactions where reagent volumes are limited, such as in microfluidic and cassettes in point of care devices.
Get In Touch With A Specialist
Have questions about a product? Want to learn more about Meridian’s molecular or immunoassay reagent portfolio? We want to hear from you!