
RNase Inhibitors
Request a Sample
Not seeing what you’re looking for? Inquire about a new product
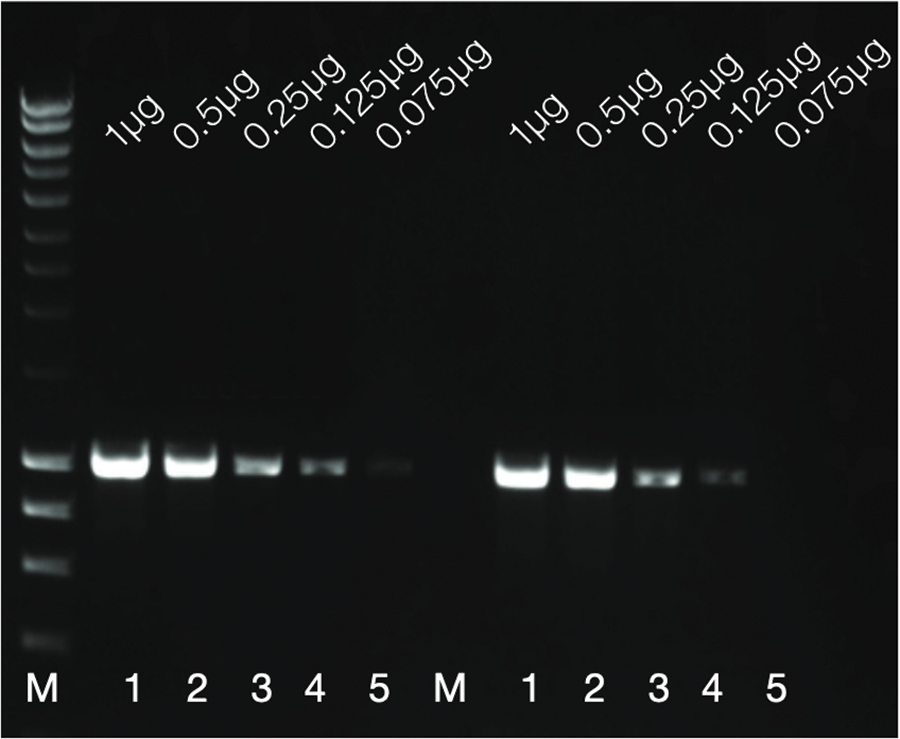
The effect of RNase Inhibitor on reverse transcriptase
Meridian RNase Inhibitors are highly efficient inhibitors of a broad spectrum of eukaryotic RNases and shows no inhibition of polymerase or reverse transcriptase activity, so can be used in cDNA synthesis or one-step PCR or quantitative PCR reactions.
A 2-fold serial dilution of HeLa cell total RNA (1 μg - 0.075 μg) was reverse transcribed in the presence (lanes 1 - 5) and in the absence (lanes 7 - 11) of RNase Inhibitor, followed by the amplification of a 1 kb fragment of the angiotensin II receptor gene under standard PCR conditions. There was no detectable difference in PCR product in the presence or absence of RNase Inhibitor, indicating that the addition of RNase Inhibitor does not interfere with the function of reverse transcriptase during cDNA synthesis.
RNase Inhibitor, MDX056
Recombinant ribonuclease Inhibitor protein which inhibits different RNases (A, B, C).
Documents & Resources
RNase Inhibitor (Glycerol Free), MDX120
Glycerol-free recombinant ribonuclease Inhibitor protein which inhibits different RNases (A, B, C).
Documents & Resources
Description
Meridian RNase Inhibitors are from a recombinant protein that inhibits different RNases (A, B, C) by binding non-covalently in a 1:1 ratio. With an association constant of 1014 M, they are useful in any applications where the presence of RNases is a potential problem. RNase Inhibitor is tested for activity, SDS-PAGE purity, and the absence of endonucleases, nickases, and exonuclease. The glycerol-free formulation ensures the compatibility of RNase Inhibitor (Glycerol Free) to lyophilized formats.
Specifications
| Description | A recombinant ribonuclease Inhibitor protein which inhibits different RNases (A, B, C) |
| Source | E. coli strain carrying the gene of RNase Inhibitor |
| Molecular weight | 50 kDa |
| Concentration | 40 U/µL |
| Association constant | 1014 M |
| Parameter | 25 – 55 °C optimum reaction temperature |
| pH range | 5.0 – 8.0 |
| Appearance | Clear, colorless solution |
| Application | RNA purification, cDNA synthesis. RT-PCR, RT-qPCR, In vitro transcription/translation, RNA sequencing, RNase protection assays, enzymatic RNA labeling reaction |
| Sample type | RNA |
| Presentation | Vials |
| Storage | -20 °C (-80 °C for MDX120) |
| Mix stability | See outer label |
| Inhibition | Total RNA incubated with RNase Inhibitor and a concentration gradient of RNase A. No degradation observed on an agarose gel |
| DNA contamination | None detected in PCR amplification with traces overlay with the negative control on E. coli and mouse genomic DNA specific targets. |
| DNase/RNase Contamination | No detectable degradation |
Catalogs & Brochures
Reagent Solutions for Molecular DiagnosticsReagent Solutions for Molecular DiagnosticsCatalog
A Comprehensive Guide to Essential Reagents for High-Throughput Molecular Diagnostic Assays (MDx)Accelerating Efficiency: A Comprehensive Guide to Essential Reagents for High-Throughput Molecular Diagnostic Assays (MDx)
FAQs: RNase Inhibitor
RNase inhibitors are commonly used as a precautionary measure in enzymatic manipulations of RNA to inhibit and control for such contaminants. Small amounts of ribonucleases can co-purify with isolated RNA or be introduced from the environment and compromise downstream applications.
Yes, to be on the safe side, we highly recommend the use of RNase inhibitors in all RT reactions, since RNases are nearly everywhere, and it is very easy to contaminate samples during RNA preparation and reaction setup. Even traces of RNase can nick the RNA, causing shortened cDNA products, low yields, and reduced RT-PCR sensitivity.
No, RNase inhibitor is a protein and will be denatured at higher temperatures.
Yes, most RNase inhibitors require reducing conditions to work properly, if the buffer does not contain DTT, the RNase inhibitor will not work. For optimal RNase inhibition, a final concentration of 1 mM DTT is required.
Get In Touch With A Specialist
Have questions about a product? Want to learn more about Meridian’s molecular or immunoassay reagent portfolio? We want to hear from you!