Alethia® C. difficile
Molecular assay for the detection of C. difficile. Alethia® provides a quick, accurate and reliable molecular assay for C. difficile detection.
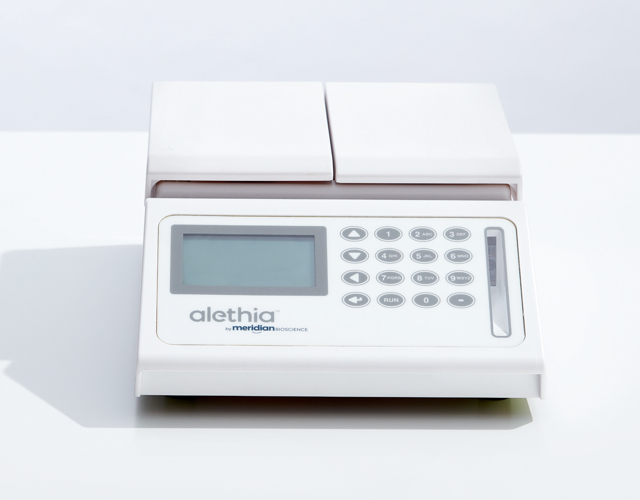

Definitive answers, confidence in results
Related Tests
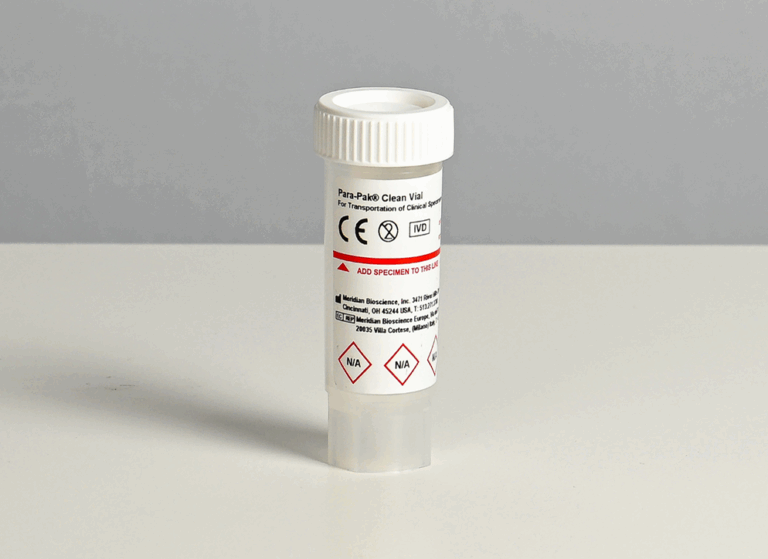
Para-Pak
The Para-Pak system provides a standardized procedure for the routine collection, transport, preservation, and culture of stool specimens for bacterial enteric pathogens. Learn More.
Related Products
Immunocard® Toxins A&B
Immunocard® C. difficile GDH

Clean Stool Transport

Support & Documents
Downloadable PDFs
FAQs
What are the differences between colonization and infection?
Colonization is more common than C. diff infection. The patient exhibits no clinical symptoms (asymptomatic) but may test positive for the C.diff organism or its toxin gene. With infection, the patient exhibits clinical symptoms and tests positive for the C.diff organism and/or its toxin.
What is the best-performing method (ie, in use positive and negative predictive value) for detecting patients at increased risk for clinically significant C. difficile infection in commonly submitted stool specimens?
Use a stool toxin test as part of a multi-step algorithm (ie, glutamate dehydrogenase [GDH] plus toxin; GDH plus toxin, arbitrated by nucleic acid amplification test [NAAT]; or NAAT plus toxin) rather than a NAAT alone for all specimens received in the clinical laboratory when there are no pre-agreed institutional criteria for patient stool submission.
What is the most sensitive method of diagnosis of CDI in stool specimens from patients likely to have CDI based on clinical symptoms?
Use a NAAT alone or a multi-step algorithm for testing (ie, GDH plus toxin; GDH plus toxin, arbitrated by NAAT; or NAAT plus toxin) rather than a toxin test alone when there are pre-agreed institutional criteria for patient stool submission.
Does detection of fecal lactoferrin or another biologic marker improve the diagnosis of CDI over and above the detection of toxigenic C. difficile? Can such a subset predict a more ill cohort?
There is insufficient data to recommend the use of biologic markers as an adjunct to diagnosis.
What were the recent changes to the CDI LabID Event Reporting?
The 2018 MDRO/CDI Protocol states that the results of the final tests that are placed in the patient’s medical record should be used to determine whether or not the event meets the CDI LabID Event definition. That means that facilities using a multi-step testing algorithm for C. difficile will be entering LabID events in NHSN based on the results of the final test in the algorithm. In 2017, the CDI testing algorithm of “NAAT plus EIA, if NAAT-positive” received the “NAAT” level of risk adjustment. Now the CDI testing algorithm of “NAAT plus EIA, if NAAt-positive” is assigned the “EIA” level of risk adjustment. Facilities using this algorithm should only enter CDI LabID events into NHSN if the results from the EIA test are positive.
What is the suggested CPT Code?
References
- https://www.cdc.gov/cdiff/clinicians/faq.html#anchor_1529601758264
- L Clifford McDonald, Dale N Gerding, Stuart Johnson, Johan S Bakken, Karen C Carroll, Susan E Coffin, Erik R Dubberke, Kevin W Garey, Carolyn V Gould, Ciaran Kelly, Vivian Loo, Julia Shaklee Sammons, Thomas J Sandora, Mark H Wilcox; Clinical Practice Guidelines for Clostridium difficile Infection in Adults and Children: 2017 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) and Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA), Clinical Infectious Diseases, Volume 66, Issue 7, 19 March 2018, Pages e1–e48, https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/cix1085
- https://www.cdc.gov/nhsn/PDFs/pscManual/12pscMDRO_CDADcurrent.pdf
Pricing
- Email: sales@meridianbioscience.com
- Phone: +1 800 696-0739
- International Sales Extension: +1 513 271-3000
