Lyo-Ready™ Genotyping Direct qPCR Blood
Lyo-Ready™ Genotyping Direct qPCR Blood has been optimized to provide highly specific allelic discrimination as demonstrated by excellent cluster separation, even in the presence of PCR inhibitors found in blood, serum or plasma. Furthermore, it can be used in a liquid or lyophilized format to create ambient-temperature stable assays, making it ideal for point-of-care (POC) devices.
Have questions about a product?
Contact us to learn more about Meridian’s molecular or immunoassay reagent portfolio. We want to hear from you!
Lyo-Ready™ Genotyping Direct qPCR Blood, MDX128
Available in 1,000 Unit or 10,000 Unit aliquots
SNPs (single nucleotide polymorphisms) or point mutations are the most common types of genetic variation and comprise the major part of phenotype diversity between individuals. SNPs can be responsible for both resistance or susceptibility to a certain disease and once individual SNPs have been identified by sequencing, they can be used for pharmacogenetics, in evaluating and predicting a patient’s response to treatment and risk of adverse events, or for diagnostics, such as in cystic fibrosis screening. Clinical screening of SNPs requires large-scale multiplexed genotyping, which traditionally relies on DNA extraction from complex samples such as blood, to achieve sensitive DNA amplification. However, blood contains several PCR inhibitors that can inhibit the reaction or reduce a reaction’s efficiency.
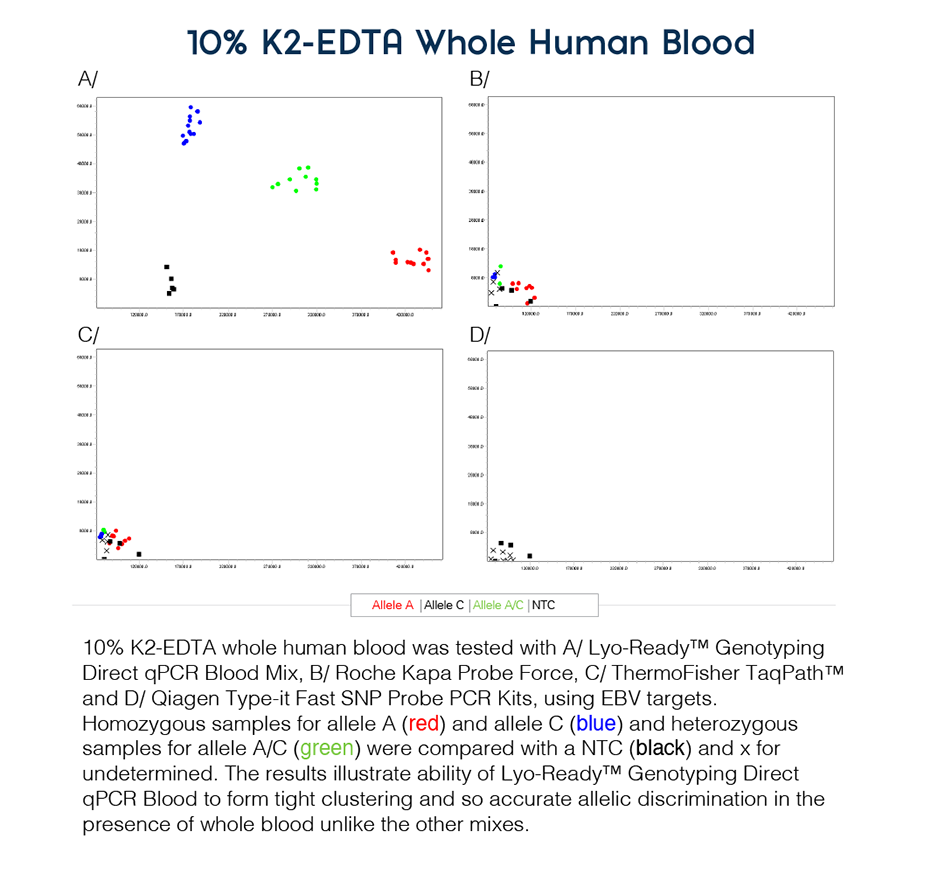
Meridian’s Lyo-Ready Genotyping Direct qPCR Blood is a 4x inhibitor-resistant mix designed for highly specific and sensitive amplification for genotyping sequence variants, even in the presence of PCR inhibitors found in blood, serum or plasma, to give exceptional cluster resolution with clear allele discrimination, even with challenging SNP targets. Furthermore, it can be used in a liquid or lyophilized format to create ambient-temperature stable assays, making it ideal for point-of-care (POC) devices.
Catalogs & Brochures
Lyo-Ready Genotyping Direct qPCR BloodLyo-Ready Genotyping Direct qPCR Blood
Air-Dryable Direct BloodAir-Dryable Direct Blood
Lyo-Ready Direct Blood MixesLyo-Ready Direct Blood Mixes
FAQs: Lyo-Ready Genotyping Direct qPCR Blood
Allelic discrimination are methods to discriminate between two or more sequence changes at a particular gene locus. Typically, one allele (“wild type” DNA sequence) is common, and the other allele (mutation) is rare. In a SNP there are 3 genotypes: – a diploid homozygote (two wild type alleles (PP)), a diploid homozygote (two mutant alleles (pp)) and a heterozygote (one wild type allele and one mutant allele (Pp)).
SNPs (single nucleotide polymorphisms) help predict an individual’s resistance or susceptibility to certain drugs (pharmacogenetics), susceptibility to environmental factors such as toxins, and risk of developing diseases. SNPs can also be used to track the inheritance of disease-associated genetic variants within families.
qPCR (Real-time PCR) enables you to screen known SNPs. The benefits of qPCR are that it is easy, accurate, and can scale to high throughput. The bioinformatic analysis is also less complex than for other technologies, such as sequencing and microarrays.
5′-nuclease (TaqMan) allelic discrimination uses a primer pair to amplify the target area and two allele-specific probes to detect your target SNP alleles and report the genotypes of your samples. Unlike normal qPCR, in genotyping the fluorescence level is only measured at the end of the PCR and the results are displayed on a scatter plot, allowing hundreds of assays to be run and analysed in parallel.
Immunoglobulin G is the major inhibitor of qPCR in blood, as it can bind to single-stranded genomic DNA, leading to increased Ct values and a lower signal. The other two main inhibitors in blood are hemoglobin and lactoferrin that affect the DNA polymerase activity and thus lowered the amplification efficiency. Hemoglobin and hematin can also cause some fluorescence quenching, particularly for FAM. In addition, inhibitors can be found in the anticoagulants used to stabilize blood samples (e.g. EDTA, citrate, or heparin).
Yes, the Lyo-Ready™ Genotyping Direct qPCR Blood can be used as a liquid mix or lyophilized and stored at ambient temperature without needing to change the reaction conditions and lyophilization/storage will not affect the sensitivity of the test.
Get In Touch With A Specialist
Have questions about a product? Want to learn more about Meridian’s molecular or immunoassay reagent portfolio? We want to hear from you!